Geothermal heat pumps are an innovative solution for efficient heating and cooling, harnessing the Earth’s renewable energy.
This article explores what ground source heat pumps are, how they operate, and the numerous benefits they offer, such as energy efficiency and energy savings.
We will examine the factors influencing their cost, long-term savings potential, and tips to secure the best deal.
Discover how this eco-friendly technology can transform your residential applications or business.
Check out: How To Install An Air Source Heat Pump
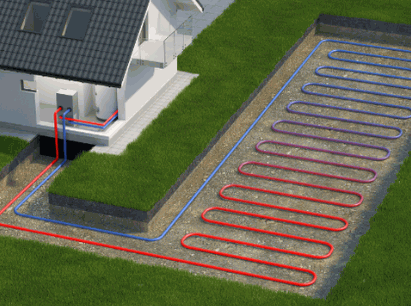
What Is A Ground Source Heat Pump?
A Ground Source Heat Pump, often referred to as a Geothermal Heat Pump, is an innovative HVAC system that uses the earth’s stable underground temperatures to provide energy-efficient heating and cooling for residential and commercial applications. This eco-friendly technology utilizes underground pipes to transfer heat, making it a sustainable option for homeowners looking to lower their energy costs while improving energy efficiency. By drawing on the relatively constant ground temperatures, these systems can significantly reduce the reliance on traditional heating and cooling methods, providing long-term savings and an impressive return on investment (ROI).
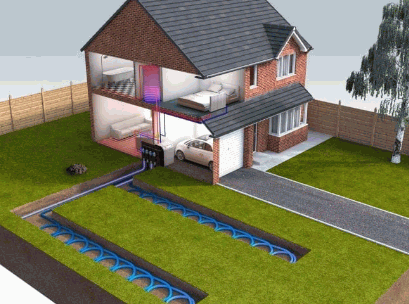
How Does A Ground Source Heat Pump Work?
A Ground Source Heat Pump operates by utilizing a heat exchanger that transfers heat to and from the ground via a fluid solution circulating through underground pipes, which can be configured as either closed-loop or open-loop systems. This innovative approach allows the system to efficiently extract heat from the earth during winter for heating purposes, and conversely, dissipate heat back into the ground during summer for cooling, making it a versatile option for various climate conditions and application types.
Understanding the mechanics of how heat transfer occurs within these systems is essential. The heat exchanger serves as the crucial mechanism that facilitates this process, enabling the movement of thermal energy through the fluid solution system.
- In closed-loop systems, a secured network of pipes is filled with a water-based solution, circulating through an insulated loop.
- Open loop configurations, however, draw water directly from a well or surface source, using it to extract or dissipate heat before returning it.
Various installation methods, such as horizontal or vertical ground loops, cater to different site conditions, ensuring optimal performance. Ultimately, the benefits of geothermal technology include reduced energy costs, lower environmental impact, and increased efficiency, making it an attractive solution for both residential applications and commercial systems.
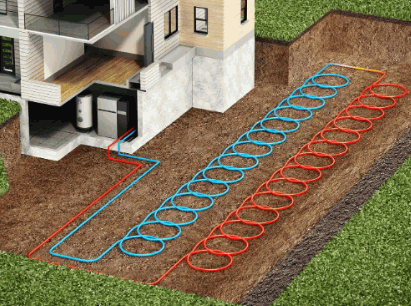
What Are The Benefits Of Using A Ground Source Heat Pump?
Using a Ground Source Heat Pump offers numerous benefits, including enhanced energy efficiency and significant energy savings for both heating and cooling purposes, making it a cost-effective choice for homeowners. These systems not only lower energy consumption but also contribute to environmental friendliness by utilizing renewable energy resources, reducing carbon footprints, and offering long-term cost savings through reduced energy bills and maintenance costs.
Energy Efficiency
The energy efficiency of a Ground Source Heat Pump is one of its standout features, often achieving efficiency ratings that far exceed traditional HVAC systems. This is attributed to the stable underground temperatures that replace the need for energy-intensive heating and cooling methods, making geothermal technology a preferred choice for energy-conscious homeowners.
In fact, these systems can achieve a coefficient of performance (COP) significantly above that of air source and energy-efficient systems, leading to substantial savings on utility bills. With impressive season performance metrics, geothermal systems maintain consistent output regardless of extreme weather conditions, delivering reliable comfort in both winter and summer months. The versatility of geothermal technology shines in diverse climates, illustrating how it can achieve energy savings.
- Reduces energy consumption by up to 70%
- Minimizes carbon footprints compared to conventional options
- Offers long-term reliability with less maintenance
By investing in such innovative systems, homeowners not only benefit from lower operational costs but also contribute to environmental sustainability and increased life expectancy of their HVAC systems.
Cost Savings
Ground Source Heat Pumps can lead to substantial cost savings on energy bills, with homeowners often noticing a decrease in energy costs soon after installation, significantly enhancing their return on investment (ROI).
These systems not only reduce monthly expenses but also can enhance property value, making them increasingly appealing for those looking to make wise financial decisions. For instance, a study conducted in the Midwest found that homeowners could save up to 50% on their heating and cooling bills after implementing geothermal technology. Over time, this results in a remarkable ROI, often recovering the initial investment within five to seven years.
- Homeowners should also explore financial incentives such as local rebates and federal tax credits that make these systems more budget-friendly.
- For example, a recent case study in California showcased a household that received a federal tax credit amounting to 30% of the installation costs, effectively reducing their financial burden.
These programs, combined with energy savings, make geothermal systems a smart choice for homeowners aiming to improve both their finances and their home’s energy efficiency.
Environmental Friendliness
Ground Source Heat Pumps are recognized for their environmental friendliness, as they utilize renewable energy from the earth, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and minimizing greenhouse gas emissions, further enhancing their appeal in eco-friendly initiatives. This eco-friendly approach not only contributes to a sustainable future but also supports various financing options and incentives aimed at promoting green energy technologies.
By harnessing the stable temperature of the earth below the surface, these systems offer an efficient alternative for heating and cooling needs. Unlike traditional methods that often rely on combustion, geothermal systems use significantly less energy, drastically lowering carbon footprints. As a result, they align perfectly with global climate goals aimed at reducing environmental impacts.
- Reduced greenhouse gas emissions
- Lower energy consumption
- Minimal disruption to the landscape
The long lifespan and low maintenance costs further enhance their appeal, making them a wise choice for both homeowners and businesses committed to sustainability and energy efficiency.

What Factors Affect The Cost Of A Ground Source Heat Pump?
Several factors influence the installation costs of a Ground Source Heat Pump, including the type of system, local labor rates, excavation requirements, and drilling costs, all of which can vary significantly based on soil conditions and climate conditions. Understanding these elements helps homeowners anticipate their total investment in geothermal systems, ensuring a well-informed decision.
Size Of The System
The size of the Ground Source Heat Pump system is a critical determinant of installation costs, as larger systems require more extensive underground piping and greater energy output to meet heating and cooling demands. Proper sizing ensures optimal efficiency and performance, making it crucial for homeowners to work with professionals to determine the right system types and sizes for their specific needs.
When evaluating the geothermal system requirements, HVAC professionals typically consider several essential factors, including ductwork compatibility. This includes:
- The square footage of the property,
- Climate zone variations,
- Insulation levels of the building,
- Occupancy patterns, and
- Existing heating and cooling systems.
Getting the sizing right not only affects energy consumption but also influences installation expenses. If the system is oversized, it may lead to higher initial costs and gradual inefficiencies, while an undersized system can struggle to maintain comfort levels, ultimately costing more energy bills.
Therefore, a thorough understanding of how to assess the appropriate fit greatly impacts overall efficiency and satisfaction.
Type Of Ground Loop
The type of ground loop selected—either a closed loop system or an open loop system—has a significant impact on installation costs and long-term performance, particularly in relation to energy efficiency. Closed-loop systems, which circulate fluid through pipes buried in the ground, are generally more expensive to install but offer greater efficiency and reliability, while open-loop systems utilize groundwater and may present varying costs depending on local regulations.
When evaluating these systems, it’s crucial to consider not only the upfront expenditure but also factors like energy efficiency, system longevity, and maintenance needs. Closed loop systems tend to provide consistent performance regardless of seasonal variations, making them ideal for areas with fluctuating temperatures. In contrast, open loop systems can be advantageous in regions with abundant groundwater but may face issues with:
- Permits and regulations
- Water quality concerns
- Potential depletion of local aquifers
Environmental impacts also play a role—the increased energy demand of closed-loop systems can be offset by their lower operational costs over time. Ultimately, each system has unique advantages and drawbacks that must align with specific local conditions, local labor, and building codes.
Installation Difficulty
Installation difficulty can significantly influence the overall costs of a Ground Source Heat Pump, as complex site conditions, including various soil conditions and climate factors, require more labor and specialized equipment for excavation and drilling. Homeowners should consider the soil conditions and potential obstacles when evaluating installation quotes from local labor providers, especially in Boulder County.
This evaluation process is crucial, as site-specific challenges can vary widely from one installation to another. Factors such as rocky terrain, high water tables, or existing structures, as well as the type of HVAC system being installed, can complicate the installation process.
- For instance, rocky soils may necessitate the use of advanced machinery, which incurs additional costs associated with system installation.
- Unexpected issues might arise during drilling or excavation, leading to delays and increased labor expenses.
Professional assessments not only help in accurately estimating the difficulty but also ensure that necessary precautions are taken to comply with local regulations. By investing in these assessments, homeowners can better navigate potential risks and manage costs effectively, making the decision to install a ground source heat pump much more manageable.
Additional Features
The inclusion of additional features, such as a variable speed compressor or specialized ductwork, can enhance the performance and efficiency of a Ground Source Heat Pump or a Dual-Source Heat Pump but may also increase installation costs.
These advanced systems, including dual-source and geothermal systems, allow for precise temperature control and better airflow distribution, which not only boosts overall comfort in the home but also promotes energy efficiency by adapting to varying thermal loads.
- Variable Speed Compressors: These adjust their speed based on demand, leading to less energy waste and lower operational costs over time.
- Specialized Ductwork: Improved duct designs minimize air leaks and ensure that conditioned air reaches all areas effectively.
These features can reduce wear and tear on the unit, leading to lower maintenance needs and extending the lifetime of the heat pump. A wise investment in such enhancements ultimately results in significant long-term savings, improved energy efficiency, and a more comfortable living environment.

How Much Does A Ground Source Heat Pump Usually Cost?
The average cost of a Ground Source Heat Pump can vary widely based on installation specifics, but homeowners can generally expect to invest between $10,000 and $30,000 for residential systems, while commercial systems typically incur higher costs based on their scale and complexity. Understanding these cost parameters is essential for budgeting and making informed decisions.
Average Cost For Residential Systems
For residential systems, the average cost of installation for a Ground Source Heat Pump typically ranges from $10,000 to $30,000, factoring in system size, type, and local labor costs. This investment yields substantial energy savings and enhanced comfort for homeowners seeking an energy-efficient HVAC solution.
The pricing often includes several essential components that can significantly impact the overall investment. Homeowners should anticipate costs associated with:
- Equipment: The heat pump unit itself.
- Installation: Labor charges, which may vary based on local rates.
- Permits: Necessary for compliance with local regulations.
Over time, this investment can lead to noticeable reductions in energy bills, with some households reporting savings of 30-50% compared to traditional heating and cooling systems, highlighting the ROI of such systems.
When comparing this renewable option, the long-term financial benefits and environmental advantages become clear, making it a compelling choice for many homeowners.
Average Cost For Commercial Systems
Commercial systems for Ground Source Heat Pumps generally involve higher installation costs, often ranging between $20,000 and $50,000 or more, depending on the specific application and size of the building. These installations tend to be more complex due to increased demand and system requirements.
When assessing the costs, it’s crucial to consider both the size of the facility and the intricacies of the system design. Commercial systems not only account for the upfront installation expenses but also for the long-term efficiency and savings that can significantly offset these initial costs. For larger buildings or those with demanding cooling and heating needs, the price tag can escalate. Their operational efficiency leads to:
- Lower energy bills over time, especially when utilizing advanced features such as a heat exchanger.
- Fewer maintenance requirements
- Potential tax incentives or rebates
Ultimately, the return on investment (ROI) for these systems, such as geothermal heat pumps and advanced dual-source setups, can surpass that of traditional HVAC solutions, making them a wise choice for future-oriented commercial users.

What Are The Long-term Savings Of Using A Ground Source Heat Pump?
Ground Source Heat Pumps provide significant long-term savings through reduced energy costs, improved energy efficiency, and lower maintenance costs, often leading to a favorable return on investment (ROI) for homeowners and businesses alike, particularly when considering innovative technologies like variable speed compressors and dual-source heat solutions. Over time, these systems prove not only to be cost-effective but also beneficial for the environment.
By utilizing the constant temperature of the earth, geothermal systems minimize energy consumption significantly compared to traditional HVAC systems, further enhancing their appeal as an energy efficient option. For instance, a residential installation in Minnesota showed an impressive 30% reduction in energy bills, leading to a payback period of just five years. In commercial settings, such as a school in Massachusetts, the adoption of geothermal technology saved approximately $25,000 annually on heating and cooling expenses, emphasizing how these systems outperform conventional methods.
- Lower operational costs
- Less frequent maintenance requirements
- Longer lifespan of equipment
The evidence highlights that investing in geothermal solutions, such as using an antifreeze solution in closed-loop systems, not only creates financial advantages over time but also contributes to a sustainable future.

How Can You Get The Best Deal On A Ground Source Heat Pump?
To secure the best deal on a Ground Source Heat Pump, homeowners should research and compare prices across different contractors while also taking advantage of available incentives and financing options, such as federal tax credits for energy-efficient systems. This comprehensive approach ensures they maximize their investment and minimize upfront costs.
Research And Compare Prices
Conducting thorough research and comparing prices from multiple contractors is crucial for homeowners looking to install a Ground Source Heat Pump, including options like an Air Source Heat Pump, ensuring they receive the best possible value for their investment. By evaluating contractor credentials and reviews, homeowners can make informed decisions about the most suitable HVAC system for their needs.
This process begins with utilizing a variety of online resources, which can offer a wealth of information about different contractors in the area and their specialization in systems like geothermal and dual-source heat pumps.
- Homeowners should look for recommendations from neighbors and friends, as personal experiences often provide trustworthy insights regarding energy-efficient systems.
- Investigating online reviews on platforms like Yelp or Angie’s List can reveal valuable feedback about past HVAC projects, including the installation of geothermal systems or air conditioning units.
- In addition, verifying a contractor’s certifications, insurance, and licensing is essential to avoid potential pitfalls.
Once a list of potential candidates is established, examining the quotes provided is critical. Homeowners should assess not just the initial cost, but also the overall value—considering factors such as warranties, materials used, and projected energy savings.
The goal is to find a contractor who offers both quality and affordability in their services.
Take Advantage Of Incentives And Rebates
Homeowners should actively seek out available incentives and rebates, including federal tax credits, that can significantly reduce the overall cost of installing a Ground Source Heat Pump, making this efficient technology more accessible. Knowing where to find these financial aids can lead to substantial savings.
Plus federal options and numerous state and local programs provide attractive financial incentives.
For instance, many states offer:
- rebates for energy-efficient home improvements
- low-interest loans
aimed specifically at renewable energy installations. Local utility companies may have their own schemes designed to encourage the use of efficient technologies.
In general, to take advantage of these incentives, homeowners need to gather specific documentation, including:
- Proof of purchase or installation
- Energy audits, if required
- Completed application forms
By understanding these elements, it becomes easier for property owners to navigate the incentives landscape and make informed decisions.
Consider Financing Options
Considering financing options for the installation of a Ground Source Heat Pump, including options for dual-source heat systems, can ease the upfront financial burden, making it possible for more homeowners to invest in this energy-efficient solution while benefiting from long-term savings on energy costs.
Various financing plans are designed to accommodate different budgets and needs, making the installation of ground-source or air-source heat pumps more accessible to homeowners.
Among the most popular choices are loans, which can lead to immediate installation and gradual repayments, enabling families to enjoy comfort without overwhelming costs.
Payment plans for energy-efficient systems offer the flexibility to spread out expenses over time, ensuring that homeowners can manage their finances without stress.
Leasing options allow individuals to utilize a Ground Source Heat Pump or an Air Source Heat Pump without the burden of ownership, making it appealing to those who prefer short-term solutions.
When evaluating these options, consider their cost-effectiveness, focusing on factors such as interest rates, potential savings on utility bills, and overall impact on property value.
Each choice has its advantages, and taking the time to analyze personal financial goals can lead to the best decision.

